If you’ve been learning about investing, you may have heard phrases like:
“Company A’s P/B is only 0.7.”
“If the P/B ratio is below 1, isn’t that undervalued?”
The P/B ratio (Price-to-Book Ratio) is one of the core metrics used to measure whether a stock is expensive or cheap compared to the company’s actual assets. Let’s break it down step by step.
✅ what is the p/b ratio?
P/B = Price-to-Book Ratio
It tells you how expensive (or cheap) a company’s stock price is relative to its book value per share (BPS) — essentially, the company’s net assets divided by the number of shares outstanding.
👉 In simple terms:
- P/B < 1 → The stock is trading below the company’s asset value (possible undervaluation).
- P/B > 1 → The stock is trading above its asset value (possible overvaluation).
📝 how to calculate p/b
The formula is simple:
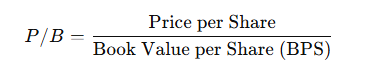
Example:
- Stock Price = $15
- BPS (Book Value per Share) = $10
- P/B = 15 ÷ 10 = 1.5
This means the company’s stock is trading at 1.5 times its asset value.
💬 why is p/b important?
✅ 1. helps identify undervalued or overvalued stocks
- P/B below 1 → Stock may be undervalued.
- P/B above 1 → Stock may be overvalued.
✅ 2. a classic value investing metric
Legendary investors like Warren Buffett often consider P/B when analyzing traditional industries such as banks, insurers, and manufacturers — where tangible assets matter most.
✅ 3. indicates safer investment opportunities
A low P/B stock that also has strong earnings and healthy financials may offer a more conservative, safer investment choice.
⚠️ But caution:
A low P/B isn’t always a good sign. It could also mean:
- The company is struggling to generate profits.
- Asset values are declining.
- The industry itself is in trouble.
That’s why P/B should always be used alongside other ratios like PER and ROE.

📊 quick summary
| Metric | Formula | Meaning | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| P/B Ratio | Stock Price ÷ BPS | Price vs. asset value | < 1 → undervalued, > 1 → overvalued |
| BPS | Net Assets ÷ Shares | Asset value per share | Needed to calculate P/B |
| PER | Price ÷ EPS | Price vs. earnings power | Complements P/B |
| ROE | Net Income ÷ Equity | Profitability of assets | Shows efficiency |
📝 final thoughts
The P/B ratio helps investors evaluate whether a stock price makes sense compared to the company’s asset base.
But remember:
No single number tells the whole story.
Smart investors use P/B together with PER, ROE, industry averages, and financial health to make balanced decisions.
👉 As a beginner, focus on learning how these ratios connect — that’s the real key to long-term success in investing.
📝 Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational purposes only. It does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. All investment decisions involve risks, and readers should conduct their own research or consult with a licensed financial advisor.
